Anti-aliasing
Aliasing can take place either in time, temporal aliasing, or in space, spatial aliasing. It may give rise to moiré patterns (when the original image is finely textured) or jagged outlines (when the original has sharp contrasting edges, e.g. screen fonts). (Wikipedia).
 Aliased image.
Aliased image.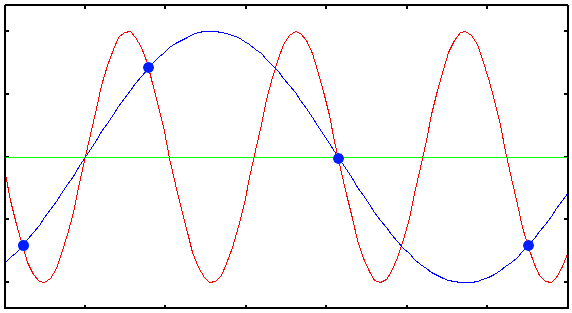
Avoiding aliasing
Anti-aliasing refers to the filters applied to an image before it is resampled (downscaled) to avoid Aliasing Artifacts. The filters remove high-frequency content from the original image reducing its Bandwidth. Therefore, the lower Sampling Density in the downscaled image is still above the Critical Sampling Distance.
Aliasing Artifacts are named after the fact that in undersampled images high spatial frequencies will return 'aliased' as low frequencies. Aliasing can easily occur in everyday pictures, and can cause disasters when periodic structures like the masonry in the following picture are present:
Strong aliasing artifacts caused by improper downscaling of this picture of the castle of St. Fargeau, France. The aliasing is most apparent in the masonry areas in the picture where high frequencies of the quasi periodic structure of the masonry are mapped to low frequencies.
A more subtle effect occurs in the areas with irregular textures: here, the aliasing effect gives rise to an overly coarse appearance of the grass, flowers and bushes.
Lastly, aliasing also gives rise to the staircase-like artifacts in the scaffolding on the left. This kind of artifact can be encountered in undersampled microscopic images of filament like structures.