Definitions
| Term | Description | |
|---|---|---|
| I-divergence | See Quality Criterion. | |
| Image size | When we are talking about image size, we mean the amount of memory the image needs to open or save, see Bytes And Bits. It could also mean the number of pixels or voxels in each dimension of the image. However, we will probably then refer to the image dimensions instead of image size to avoid confusion. | |
| Sampling distance | see Sample Size. | |
| TM | TM stands for Tikhonov-Miller. | |
| NA | NA stands for Numerical Aperture. | |
| Photon count | see Excitation Photons. | |
| Vignetting | Vignetting is an optical defect of camera lenses. It is the effect in images where the image border and especially corners are darker than the center. The amount of vignetting depends on the lens used for imaging. In general the more expensive, the less vignetting. For more information, see e.g. Vignetting. | |
| PSF | PSF stands for Point Spread Function. | |
| CE | CE stands for Huygens Compute Engine. The Huygens Compute Engine is the image processing engine shared by most of the Huygens Software. | |
| Join | Combining two images in one multichannel image, is called joining. See more Joining or splitting channels | |
| Split | Extracting all the channels from an image is called splitting, see more at Joining or splitting channels | |
| OME | OME stands for Open Microscopy Environment. | |
| MLE | MLE stands for Maximum Likelihood Estimation. | |
| TIRF | TIRF stands for Total Internal Reflection fluorescence. | |
| QMLE | QMLE stands for Quick Maximum Likelihood Estimation. | |
| ICTM | ICTM stands for Iterative Constrained Tikhonov Miller. | |
| CMLE | CMLE stands for Classic Maximum Likelihood Estimation and is the most general Restoration Method available in the Huygens Software. See Maximum Likelihood Estimation for more details. | |
| ICS | ICS stands for Image Cytometry Standard, a file format for microscopy images. | |
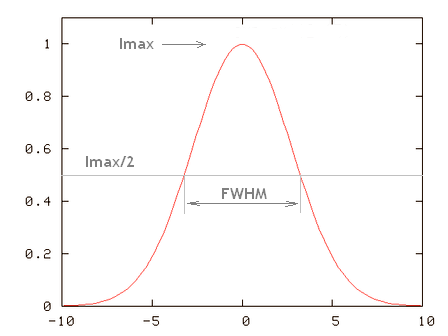
| FWHM | FWHM stands for full-width at half-maximum. See Half Intensity Width. | |
| ELMI | ELMI stands for European Light Microscopy Initiative. For more information: http://www.embl.org/elmi/. | |
| Third Harmonic Generation | Third Harmonic Generation is like Second Harmonic Generation but involving three excitation photons instead of just two. | |
| OTF | OTF stands for Optical Transfer Function. The optical transfer function of an optical device is the Fourier Transform of its Point Spread Function. | |
| Regularized method | A regularized method is a Non Linear Iterative Method for Image Restoration that uses a Regularization Parameter. | |
| FFT | FFT stands for Fast Fourier Transform, an algorithm to numerically calculate Fourier Transforms of digital signals. The Tcl Huygens command to calculate it is fft. |
|
| Nyquist criterion | The Nyquist criterion determines the minimal Sampling Density needed to capture all information from the microscope into the recorded image. This sampling density is the Nyquist Rate. | |
| Critical Sampling Distance | The Critical Sampling Distance is the Sampling Distance corresponding to the Nyquist Rate. Images obtained with sampling distances larger that this suffer from UnderSampling. | |
| Pinhole spacing | The pinhole spacing (in um) is the distance between the pinholes in a spinning disk. As is the case for the Back Projected Pinhole Radius, the pinhole spacing must be divided by the system magnification. | |
| 2D | 2D means two-dimensional. The Huygens Software can restore 2D Wide Field Microscope images, see the FAQ Is deconvolution on 2D or 2D-time images possible?. See also PiXel and 3D. | |
| Single Channels | A single channel image (or Time Series) is, in a general case, a 2D or 3D image (or series of images) in which only one Emission Wavelength was registered. See Multi Channel. | |
| GUI | GUI stands for a Graphical User Interface and it is an interface to a computer program that allows the user to interact with it by using graphical widgets (like bars, buttons and panes) on a screen as opposed to simply textual menus or a command line. | |
| Raw data | Raw data are data prior to image restoration, with all the acquired blur and Photon Noise. These raw images should not be altered by any mean before deconvolution, as the restoration needs all the information contained in them, including all the noise. | |
| Specimen embedding medium | A specimen embedding medium is the medium in which the specimen being measured is embedded. Its optical activity is taking into account by the Medium Refractive Index. If your medium is not listed you can enter its refractive index manually. | |
| Deconvolution parameters | Also called Restoration Parameters in the Huygens Software, they establish the conditions for the different deconvolution algorithms. See Restoration Parameters. | |
| LIF | LIF stands for Leica Image File. SVI's software reads multi-channel LIF files, with resolutions of both 8-bit and 16-bit, with arbitrary order of dimensions. All relevant microscopic parameters needed for deconvolution are read from the XML-header inside the LIF file. | |
| Datatype | The basic data types used for VoXels values in images by the Huygens Compute Engine are: unsigned Byte Type, signed Integer Type, 32-bit Float Type, 2 * 32-bit Complex Type |
|
| Binary type | It is an unsigned 1 bit type. The valid range is therefore simply 0 or 1. These type of images are usually used for mask images. | |
| Byte type | It is an unsigned 8 bit type. The valid range is therefore integers from 0 to 255. Read more at Byte Type. | |
| Integer type | It is a signed 16 bit type. The valid range is therefore integers from -32768 to 32767. Read more at Integer Type, especially if you are interested in the 16 bit TIFF file format. | |
| Float type | It is a signed 32 bit type (single precision). The valid range is therefore floating point reals, positive and negative, with absolute values ranging from 1.17549435E-38 to 3.40282347E+38, including the zero. Read more at Float Type. | |
| Complex type | Complex numbers are represented by using two Float Type numbers, one for the real part and another one for the imaginary part. Read more at Complex Type | |
| Sparrow criterion | The Sparrow limit is the distance between such point objects of equal intensity at which a dip half way between them ceases to be visible in the superposition of their images (the first two derivatives of the intensity curve along the connecting line become zero). | |
| IMLE | IMLE stands for Iterative Maximum Likelihood Estimation. The Iterative Maximum Likelihood Estimation Restoration Method is an obsolete form of the Classic Maximum Likelihood Estimation (CMLE) method, that is kept in the Huygens Software for backward compatibility. | |
| Pixel | A pixel (short for picture element, using the common abbreviation "pix" for "picture") is one of the many tiny dots that make up the representation of a picture in a computer's memory (Wikipedia). In the context of 3D fluorescence microscopy, the pixel (representing a 2D element) becomes a VoXel (representing a 3D element). | |
| Voxel | Voxel is the short for volume pixel, the smallest distinguishable box-shaped part of a 3D image (Wikipedia). It is the 3D equivalent of the 2D pixel. See also 3D and ThreeDeeImage. | |
| Wavelength | Wavelength is the distance between two consecutive crests of a wave. In the optical range it is usually measured in nanometers (nm). In optical microscopy involving fluorescence, two wavelengths are important: the Excitation Wavelength and the Emission Wavelength. Read more at Wavelength. | |
| Emission wavelength | The emission wavelength is the WaveLength of the radiation emitted by the object being measured, coming from the fluorescent dyes. The fluorescent emission is caused by a radiation source with a given Excitation Wavelength. | |
| Excitation wavelength | The excitation wavelength is the WaveLength of the radiation (usually coming from a laser line) used to stimulate fluorescence in the measured object. The stimulated dye will emit radiation with a particular Emission Wavelength. | |
| RGB color | The RGB (Red, Green, Blue) model defines a color in the amount of red, green and blue. Typically these amounts range from 0 - 255, where 0-0-0 represents black and 255-255-255 represents white. Using this representation of colors, 16,581,375 different colors can be distinquished. Hexadecimal numbers are used to represent an RGB-color in 6 digits, mostly for HTML coding or in photo editing programs. | |
| HSV color | The HSV (Hue, Saturation, Value) model defines a color in terms of three constituent components: Hue, the color type (such as red, blue, or yellow), Saturation, the "vibrancy" or "purity" of the color, and Value, the brightness of the color. See the Wikipedia. HSV is also often called HSB, with B for Brightness. Also the HSL combination is used, with L for Lightness. This is however slightly different from HSV: where HSV goes from black to color, HSL goes from black to color to white. Therefore V = 1/2L. Read more at Wikipedia. | |
| Color depth | Color depth or bit depth, is a computer graphics term describing the number of bits used to represent the color of a single pixel in a bitmapped image or video frame buffer. (Wikipedia). The larger the color depth of an image, the larger the Dynamic Range you can store in it. | |
| Deconvolution Recipes | The Deconvolution Recipes is a guide to image restoration for SVI customers. It contains specialized knowledge and tips on topics like recording microscopic images, how to get a Point Spread Function and information on Doing Deconvolution. | |
| OIF | OIF stands for Olympus Image Format. A file with the extension .oif is an Olympus Fluoview TIFF format file. Olympus Fluoview TIFF format (FM Multi-tiff) is an extension of the standard TIFF format that introduces some new TIFF tags. The Huygens Software can read this special type of TIFF images that can store multiple 2D planes in a 3D stack. | |
| Paraxial simplification | The paraxial simplification is an approximation to the full equations of optics that is valid in the limit of small angles from the optical axis. It does not consider the vectorial character of light, and only takes care of amplitudes. See http://scienceworld.wolfram.com/physics/ParaxialApproximation.html | |
| Trilinear interpolation | Trilinear interpolation is the process of taking a three-dimensional set of numbers and interpolating the values linearly, finding a point using a weighted average of eight values. (Wikipedia). | |
| Half Intensity Width | The half-intensity width (HIW) (or more precisely the Full-width at half-maximum (FWHM)) of a curved function is the distance between the points where the intensity is half of the maximum one. The HIW of a Point Spread Function is a good estimation of the device Spatial Resolution. | |
| HuEss | HuEss stands for the product Huygens Essential. | |
| HuPro | HuPro stands for the product Huygens Professional. | |
| HuScript | HuScript stands for the product Huygens Scripting. | |
| HuCore | HuCore stands for the product Huygens Core. | |
| HRM | HRM stands for Huygens Remote Manager. The Huygens Remote Manager (HRM) is a web task manager for servers that acts as an interface to Huygens Core to do online, multiuser, batch deconvolution. | |
| Variance | For a series of (xi) elements, the variance is calculated as $$ {\text var}\ =\ \frac{\sum (x_i - x_{avg})^2}{N} $$ with $$x_{avg}$$ the average value of all the $$x_i$$, and $$N$$ the total number of elements in the series. Compare with CoVariance, that relates two different series of elements. See also WikiPedia. |
|
| Lens Immersion Medium | The lens immersion medium is the medium in which the microscope objective is immersed. Its optical activity is taken into account by the Lens Refractive Index. Objectives are designed to work on particular immersion media, like oil, water or air. The lens immersion medium is directly related to the Numerical Aperture of the objective. | |
| LSM | LSM stands for Laser Scanning Microscope. The Zeiss LSM file format is an extended multi page TIFF-format that can hold more than the three standard TIFF data channels. This extension is useful for Multi Channel microscopy images. Read more about LSM on wikipedia and also see ICSfile Format and the Huygens File Formats. | |
| Bit (b) | One bit is the smallest unit of information. In a binary numerical system it is what you can represent with a one or a zero. See Bytes And Bits for an example. | |
| Byte (B) | Nowadays one byte is always 8 bits. Therefore, in a 16 bit image every pixel intensity is represented by 2 bytes. See Bytes And Bits for an example. | |
| STED | STED stands for STimulated Emission Depletion microscopy. Because this techniques overcomes the limitations caused by the defraction of light it is a form of super-resolution microscopy. Read more at Huygens STED Software or at wikipedia (STED, super-resolution microscopy) | |
| Hot pixels | Hot pixels are produced by individual sensors on the CCD camera with higher than normal rates of charge leakage. They appear as abnormally bright pixels of light on long exposed images. Read more at Hot Pixels. | |
| Baseline | See Blacklevel. | |
| Blacklevel | Blacklevel, also called baseline, is the output of the photo-multiplier if no light is coming through. Read more at the wikipage Blacklevel. | |
| 3D | 3D means three-dimensional and it refers to the distribution of a physical magnitude in a volume in space. Read more at 3D and 3D-images. | |
| TIF or TIFF | TI(F)F stands for Tagged Image (File) Format. TIFF is a flexible and adaptable file format. It handles data through the inclusion of "tags" in the file header. Read more at TIFF. | |
| ZVI | ZVI stands for Zeiss Vision Image, developed by Carl Zeiss. You can use it to save images including time lapse or Z-stack images. The Huygens Software reads the ZVI file format. Read more at File Formats. | |
| HDF | HDF stands for Hierarchical Data Format and is the primary Huygens format for reading and writing. It is a versatile file format originally developed at the NCSA, and currently supported by the non-profit HDF Group. Read more at HDF5. | |
| H5 | The H5 file format is a Huygens microscopic HDF format, fully based on the HDF format. Our intention with the H5 format is that it should be possible to open and view the images and metadata with standard tools like 'hdfview'. It is also possible to open and view these format files with Matlab or Mathematica. Read more at HDF5. | |
| 2D Histogram | In image processing a 2D histogram shows the relationship of intensities at the exact position between two images, e.g. two channels. It can be very useful to detect some properties of your image, like clipping, correlation, intensity proportion etc. Read more at TwoChannelHistogram | |